Plunge pools are naturally occurring depressions found typically at the base of waterfalls. They're a result of the continuous erosive action of cascading water and swirling rock fragments, greatly enhanced by the force and speed of the waterfall. The type of bedrock plays an essential role too; sedimentary rocks, for instance, erode faster and create larger, deeper pools. Water pressure, temperature swings, and human activity also contribute to the erosion process that forms these pools. By comprehending the intricate workings of these erosion processes, you're on your way to grasp how plunge pools affect aquatic ecosystems and contribute to our planet's geological richness.
Defining Plunge Pools
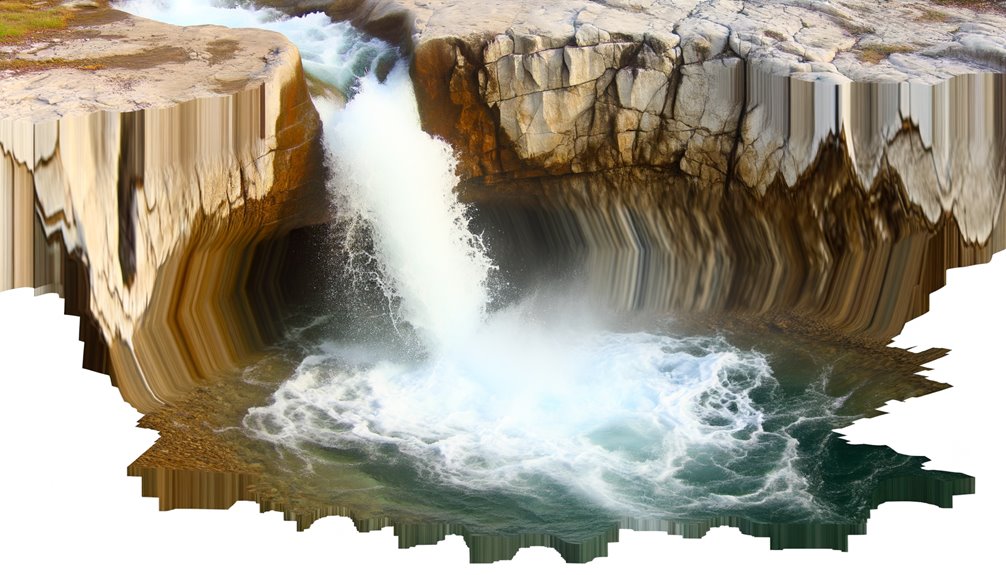

A plunge pool, an essential element in the domain of physical geography, is a natural depression or hole formed at the bottom of waterfalls due to the erosive action of falling water and the swirling motion of smaller fragments.
These plunge pool characteristics are critical to understand how they come into being. The plunge pool formation process is a demonstration of the powerful forces of nature, a synergy of hydraulic action and abrasion.
You'll find that these pools are typically deeper near the waterfall, owing to the intense erosive force there. The bedrock type also influences pool depth and size. Sedimentary rocks, for instance, erode faster, creating larger, deeper pools.
The Role of Waterfalls
While you might initially think of waterfalls as merely scenic spectacles, they're instrumental in the formation of plunge pools.
Waterfall formation and plunge pool dynamics are closely interlinked. Here's how:
- The waterfall's vertical drop: The force generated by water falling from a height erodes the bedrock, creating a depression.
- Water velocity: The speed of the water amplifies the erosion process, deepening the plunge pool.
- Water volume: Higher volumes of water increase the rate of erosion, accelerating the plunge pool's formation.
- Rock type: The bedrock's composition affects how quickly it erodes. Softer rock types erode faster, speeding up the creation of plunge pools.
In essence, the dynamics of a waterfall considerably influence the formation and depth of plunge pools.
Understanding Erosion
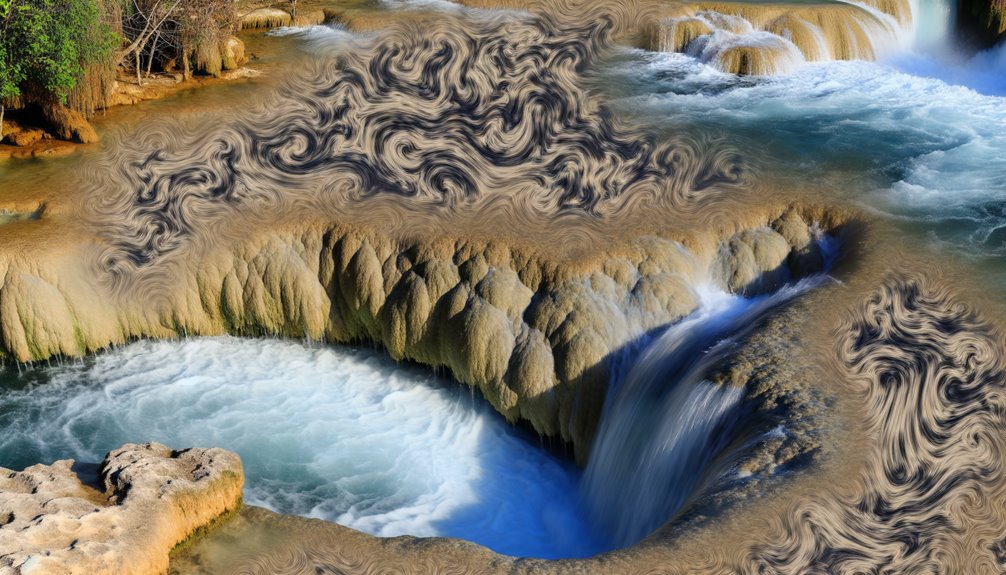

You must grasp the mechanics of natural erosion to understand how plunge pools form.
Take into account the impact of water flow, which gradually wears away the riverbed, leading to the creation of these fascinating natural formations.
It's not just about water's power, but also its persistence over time that shapes our environment.
Mechanics of Natural Erosion
Despite their serene appearance, plunge pools are the result of a powerful and relentless force: erosion. This natural process, influenced by geological factors, tirelessly reshapes the Earth's surface.
Consider these steps in the mechanics of natural erosion:
- Rainfall loosens soil particles which are carried away by the water's flow.
- Wind sweeps up fine sediment, depositing it elsewhere.
- Gravity pulls rocks and debris down slopes, causing landslides.
- Waves batter and break down coastlines, creating cliffs and caves.
These processes work together, carving out the depression that becomes a plunge pool.
With time and the relentless power of nature, water's impact hollows out the rock, creating a tranquil haven amidst the tumultuous process of erosion.
Impact of Water Flow
Understanding the impact of water flow is pivotal to fully grasp how erosion forms plunge pools. You should know that water velocity and flow patterns play critical roles here.
When water flows over a cliff or steep incline, it's not just a gentle trickle. The speed or velocity of the water greatly affects erosion rates, and the faster it moves, the more soil and rock it can carry away.
Flow patterns also matter. Water tends to follow the path of least resistance, carving out channels and gullies over time. In areas where the water flow is concentrated, such as in these channels, erosion occurs more rapidly, leading to the formation of deep plunge pools.
Impact of Water Speed
While the beauty of plunge pools can captivate many, it's the force and speed of the water that truly shapes their unique characteristics.
You see, water speed, or velocity, plays a crucial role in plunge pool formation.
- Erosion: High water velocity increases erosion, carving out the pool.
- Sediment Transport: Faster water can carry larger sediment, deepening the pool.
- Turbulence: Speed affects the water's turbulence, impacting pool shape.
- Energy Dissipation: The faster the water, the more energy it dissipates upon impact, influencing pool dimensions.
As you can see, water speed is a critical factor in shaping plunge pools.
It's not just about the quantity of water, but the pace at which it moves that determines the final outcome.
Significance of Pool Depth
As we shift our focus to pool depth, you'll see that it's influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including water velocity, geological features, and seasonal variations.
This depth, in turn, has profound impacts on the ecosystem it houses. From microorganisms to larger fauna, the depth of a plunge pool shapes its biodiversity and overall health.
Factors Influencing Pool Depth
If you've ever wondered why some plunge pools in nature are deeper than others, several key factors play a role in this fascinating phenomenon.
- Geological Factors: The type and structure of the bedrock can greatly influence pool depth. Harder rocks resist erosion, leading to shallower pools, while softer or fractured rocks may erode more readily, creating deeper pools.
- Water Velocity: Faster flowing water carries more energy to erode the rock, potentially creating deeper pools.
- Water Volume: Larger volumes of water can cause greater erosion, potentially leading to deeper pools.
- Water Temperature: Warmer water can speed up chemical weathering processes, contributing to the erosion of the rock and potentially influencing the depth of the pool.
Understanding these factors can help us appreciate the complex processes that shape our natural world.
Depth Impact on Ecosystem
Given the depth of a plunge pool, it's essential to understand its significant influence on the ecosystem.
The depth diversity it provides is instrumental in creating varied habitats for aquatic life. Deeper parts accommodate species that thrive in cooler, darker conditions, while shallower areas support those preferring warmer, well-lit environments.
It's not just about temperature and light, though. Depth also affects water pressure, oxygen levels, and nutrient availability.
So, by providing these different 'zones', a plunge pool contributes to habitat stability. Its depth variations guarantee a healthy balance of species, each occupying its best-suited niche.
This balance, in turn, enhances the pool's resilience to environmental changes.
Influence of Rock Types
Three primary rock types greatly affect the formation and characteristics of plunge pools. These are sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks.
- Sedimentary Rocks: These rocks influence the shape and size of plunge pools. Their composition, mainly sand, silt, and clay, makes them susceptible to erosion, leading to pools with irregular shapes and varying depths.
- Igneous Rocks: Known for their resistance to erosion, they result in more rounded and deep plunge pools.
- Metamorphic Rocks: The strength and composition of these rocks influence the formation of plunge pools. They form under high pressure and temperature, resulting in pools with unique shapes and sizes.
- Rock Composition and Geological Formations: These factors, combined with water flow, dictate the formation of plunge pools.
Understanding the influence of rock types helps predict the patterns and longevity of these natural pools.
The Cycle of Sedimentation
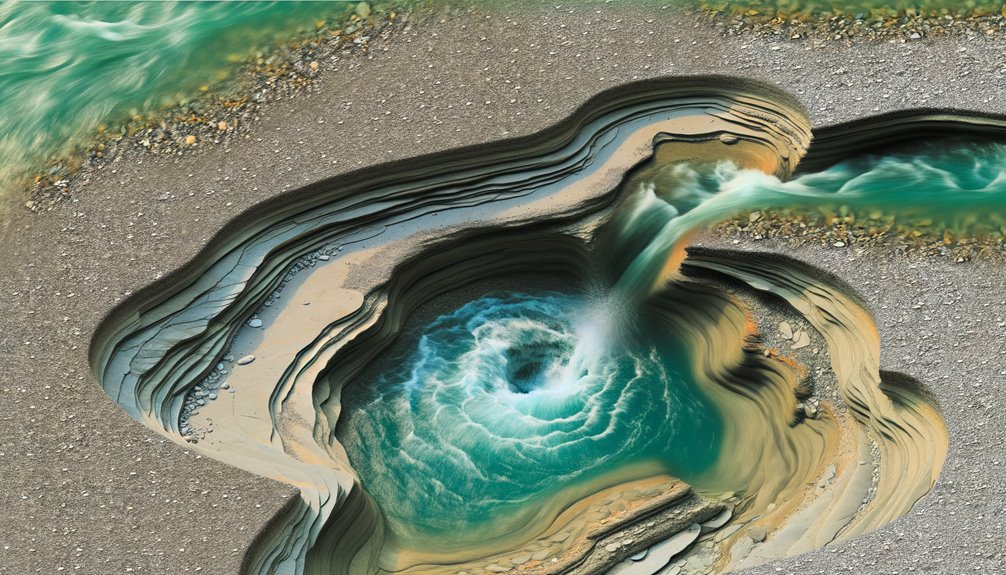

While you may well appreciate the visual appeal of plunge pools, understanding the cycle of sedimentation can enhance your comprehension of their formation and evolution.
This cycle involves both sediment transport and sediment deposition. Water's current carries small rock and soil particles downstream, making up the sediment transport phase. As the water flow decreases, that's when sediment deposition occurs, with the particles settling at the bottom of the plunge pool.
This cycle repeats over time, gradually deepening the pool. However, the rate of sedimentation isn't constant. It's influenced by factors like water velocity and sediment size.
Effects of Weather Conditions
If you've ever observed a plunge pool, you've likely noticed how it changes with the weather.
The effects of weather conditions on these natural formations are significant and can be categorized into these four main areas:
- Rainfall: Heavy rains can increase erosion around the plunge pool, altering its depth and width.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures, particularly freezing conditions, can cause the pool's water to expand and contract, leading to changes in its structure.
- Wind: Strong winds can cause waves in the pool, contributing to its erosion and sedimentation.
- Seasonal Changes: Overall, weather patterns and climatic changes across seasons can drastically affect the formation and transformation of plunge pools.
Understanding these effects provides a deeper insight into the dynamic nature of plunge pools.
Plunge Pools and Ecosystems
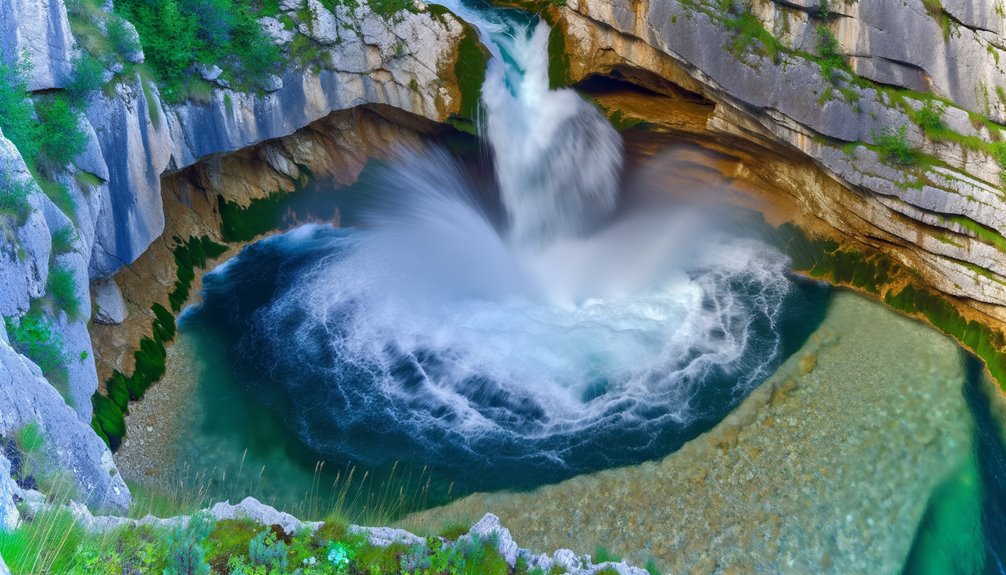

Building upon our understanding of how weather impacts plunge pools, let's turn our attention to their role in ecosystems.
Plunge pools contribute notably to ecosystem diversity. They're natural aquatic habitats, home to a variety of life forms, from tiny microorganisms to larger aquatic species. The unique environmental conditions within these pools, such as temperature, water flow, and nutrient availability, foster a diverse, vibrant community of organisms.
Additionally, plunge pools act as 'stepping stones' for migratory species, offering temporary refuge and resources. They also play an essential role in nutrient cycling, influencing the overall health and functionality of wider aquatic systems.
Understanding these interactions is key to appreciating the value of plunge pools in sustaining biodiversity.
Famous Natural Plunge Pools
In regard to natural beauty, few features are as breathtaking as famous plunge pools scattered across the globe.
These iconic plunge locations, carved by nature's forces over millennia, are as diverse as they're stunning.
- Devil's Pool, Zambia: Perched on the edge of Victoria Falls, it's a heady mix of serene waters and thunderous cascades.
- Fairy Pools, Scotland: These crystal-clear pools, nestled amid the Cuillin Hills, offer a bewitching sight.
- Giola Lagoon, Greece: A natural sea pool, framed by rock formations, it's a Mediterranean gem.
- Ik Kil Cenote, Mexico: A sinkhole filled with turquoise waters, it's an evidence of nature's artistic prowess.
You'll find that each of these famous plunge pools offers a unique blend of beauty, thrill, and scientific intrigue.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Plunge Pools Safe for Swimming?
Yes, you can safely swim in plunge pools, but it's crucial to be aware of possible natural hazards.
These could include strong currents, sharp rocks, or unexpected depth changes.
It's always a good idea to check out the pool's conditions before diving in.
What Maintenance Does a Natural Plunge Pool Require?
When maintaining a natural plunge pool, you're faced with unique challenges.
You've got to monitor water quality regularly, guarantee natural filtration systems are working efficiently, and take care of any debris.
It's not just about keeping it clean, but also making sure it's safe for use.
Regular checks on the pool's ecosystem balance are essential too.
How Long Does It Take for a Plunge Pool to Form Naturally?
It's tough to give an exact time frame for how long it takes to naturally form a plunge pool.
It largely depends on geological processes such as natural erosion, water flow rate, and the type of rock involved.
However, you're looking at a process that spans thousands, if not millions, of years.
Nature isn't in a rush, it's a slow and steady process that results in the beautiful plunge pools we see today.
Can Plunge Pools Disappear Over Time?
Yes, plunge pools can disappear over time.
You're not just whistling Dixie, it's all about plunge pool erosion and geological processes.
Rainfall, wind, and flowing water gradually erode the rock, altering the pool's shape and depth.
Over a long period, the pool may completely erode away.
It's a slow but relentless process, showing how even the seemingly permanent features of our planet are constantly changing.
How Does Climate Change Affect the Formation of Plunge Pools?
Climate change considerably impacts plunge pool formation. Warmer temps can increase glacial melt, leading to stronger water flow that intensifies erosion processes. This can expedite the creation of plunge pools.
On the flip side, drought conditions can lessen water flow, slowing down erosion and plunge pool formation.
